Knowledge Graph
The Glean Knowledge Graph is a powerful tool that forms the backbone of Glean's enterprise search platform. It is designed to provide users with the most personalized and relevant results for their queries.
About the Glean Knowledge Graph
Glean's unique search engine operates based on a real-time model of your enterprise's indexed information – the enterprise knowledge graph.
This system involves three key pillars: Content, People, Activity.
flowchart TB
title["Knowledge Graph"]
subgraph Activity
creation["Creation date"]:::yellow
history["Editing history"]:::yellow
Comments:::yellow
Searches:::yellow
Clicks:::yellow
Shares:::yellow
Views:::yellow
end
subgraph People
Identities:::salmon
Roles:::salmon
Teams:::salmon
Departments:::salmon
Groups:::salmon
manager["Reporting line"]:::salmon
Tenure:::salmon
end
subgraph Content
Documents:::teal
Messages:::teal
Tickets:::teal
Emails:::teal
Assets:::teal
Images:::teal
Entities:::teal
end
title --> Content
title --> People
title --> Activity
classDef teal stroke:#A2BA25,fill:#D0E26F,color:#333;
classDef salmon stroke:#FF935F,fill:#FFBE9F,color:#333;
classDef yellow stroke:#FAC748,fill:#FEE58F,color:#333;Content
Filling the knowledge graph with content begins with our easy-to-use 100+ connectors. Each connector is tailor-made for each application’s unique data model and API endpoints, requires no additional professional services to use, and is fully permissions-aware – ensuring all accessibility and sharing protocols are strictly followed for each source.
Through these connectors, Glean's content crawler searches over every part of a piece of content, not just the title. This involves relevant item content (titles, body copy, comments, media, etc.), as well as metadata (file creator, time of creation, update history, file type, folder structure, etc.)
flowchart LR
Glean((Glean)):::glean
Communication
Docs["Documents & Wikis"]
Storage["Cloud Storage"]
CRMs
Ticketing["Tasks & Ticketing"]
Code["Code & Dev tools"]
Glean --- Communication & Docs & Storage & CRMs & Ticketing & Code
classDef glean stroke:#9297F4,fill:#343CED,color:#fff;All of these elements, stored within the knowledge graph’s index, become readily searchable. Customizable weights can also be set for specific categories to influence search results. Facet search results can be tuned based on metadata fields specific to each app.
Permissions can also be individually set for specific items. Files can be selectively included or excluded from Glean's crawl system by specifying asset IDs or by a broader categorization, such as item containers (folders or drives).
The content crawl strategy is also completely tunable according to your organization's preference. Adjust crawl cadence, assign blackout hours to avoid peak work hours, and shift between different crawl methodologies to ensure your knowledge graph contains the most relevant and up-to-date information throughout the day.
People
One out of ten enterprise searches are about people. It makes good sense – workers want to know exactly who they're working with, what their role is, and what they have most recently worked on. Glean facilitates this by aggregating data across multiple tools, providing a comprehensive and information-rich view of anyone in the company.
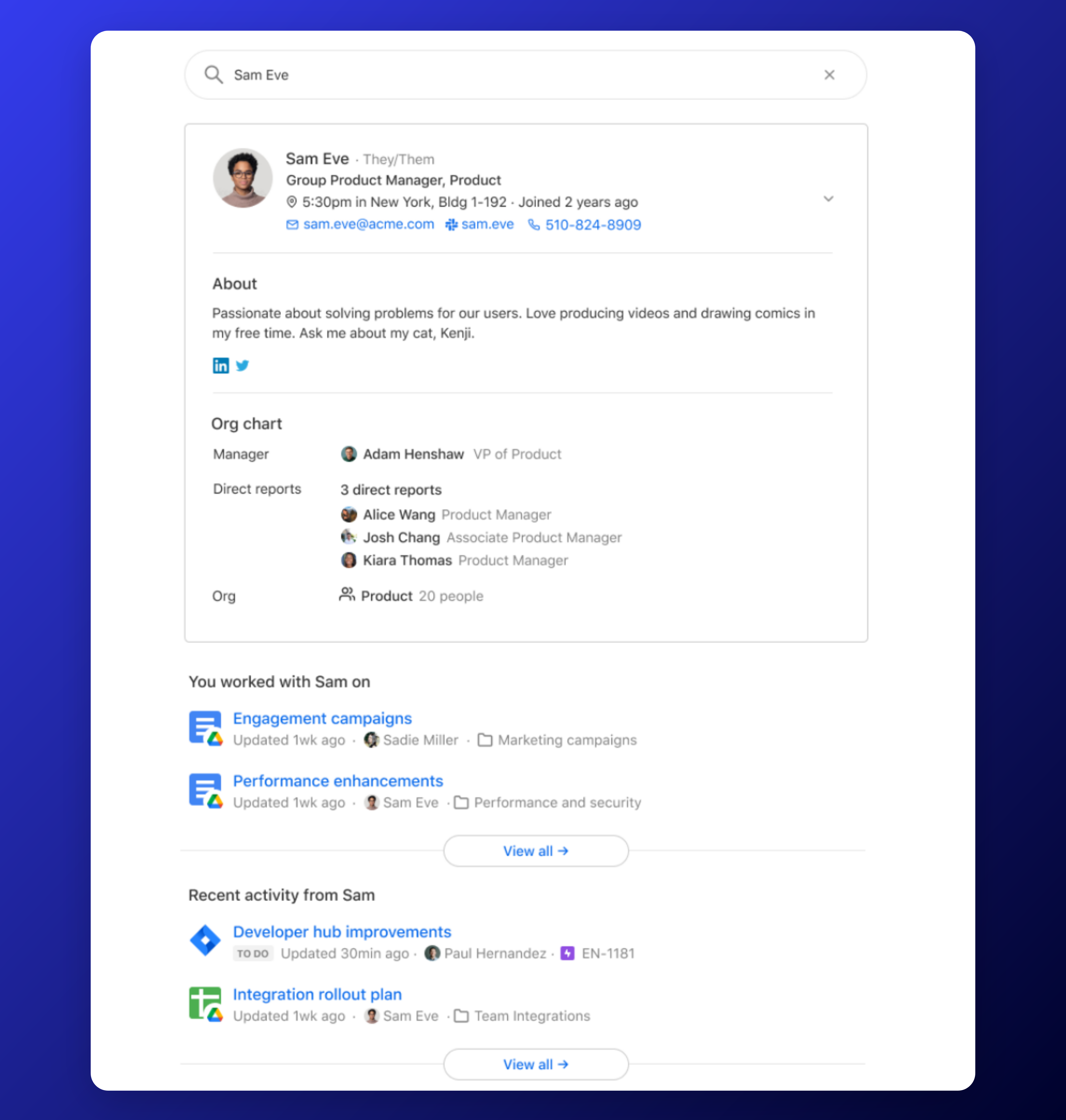
Our engine is also capable of providing deeply personalized and permissions-aware results, especially as it better understands each individual’s role within an organization.
Glean builds each enterprise's knowledge graph with a deep understanding of the people within, such as what their role is which team they're on, their tenure, and location. Our system is then capable of constructing a unified identity for each person across all apps, along with a holistic organization structure that understands everything from each person's closest collaborators to what projects they have most recently worked on.
The underlying data model and individual sources of information used to build these profiles can be customized according to preference.
Activity
Glean collects activity data from several apps (Teams, Slack, email, plugins, Chrome extension, etc.) to index critical signals required for better search personalization and relevance. We only collect activity on sources connected to the product. As mentioned, none of this activity information ever leaves your exclusive GCP project and follows strict data protection rules to ensure privacy.
The activity information is used in two ways:
-
Learning what information matters most to better personalize results for users – individual user data does not leak over to any other user.
-
Improving personalization for a collection of users – privacy thresholds ensure data is only collected when we see a common data point across multiple users.